Edge Computing
Moving Intelligence to the Edge
Edge computing involves processing data closer to its source, rather than relying on a centralized data center. This approach reduces latency, bandwidth usage, and dependence on cloud infrastructure, making it ideal for a variety of use cases.
Edge computing can be deployed in various circumstances. Autonomous vehicles, Rich web content delivery, Internet of Things, Software as Service, Voice Assistants, Predictive maintenance machines or services, Traffic Management, etc. All of these need real time data processing and reduced latency.
One prominent application is in the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), where edge computing enables real-time data analysis and decision-making.
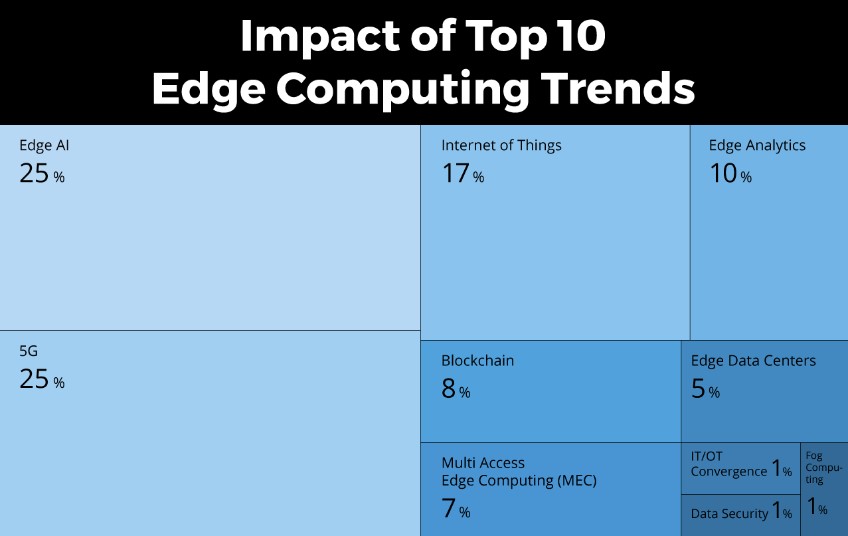
Top 10 Edge Computing Trends Impacting 2024
Key trends include Edge AI, which moves computing closer to edge devices for quicker data processing and reduced latency. The introduction of 5G technology promises unprecedented speed and minimal latency, enhancing communication. IoT technology drives better connectivity and data sharing, facilitating efficient data collection and decisions. Real-time edge analytics allow for instant operational insights, while blockchain technology secures data in edge environments. Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) alleviates network congestion by introducing cloud functionalities nearer to data sources. Edge data centers and IT/OT Convergence improve local data handling and operational efficiency, respectively. Similarly, fog computing decentralizes processing and storage, optimizing data proximity.
Seeking the Ideal Distributed Computing Solution?
As the Internet of Things, Mobile- and AI Edge evolves, the rise of edge computing becomes inevitable. ServerDirect assists you in finding the ideal distributed computing framework that places enterprise applications closer to data sources, such as IoT devices or local edge servers. Such strategic positioning of data at its source can offer substantial business benefits, including quicker insights, improved response times, and enhanced bandwidth availability. We are committed to helping you identify the server solution that best meets your needs.
Edge Computing Solutions
Edge Computing vs Traditional Cloud Computing
Edge computing offers distinct advantages over traditional cloud computing, highlighted by the following key points:
Low Latency: By processing data closer to its source, either at the network's edge or directly on devices, edge computing significantly cuts down the data travel distance. This reduction in latency speeds up response times for applications demanding real-time processing, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and real-time analytics, ensuring swift and efficient operation.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Local data processing at the edge means that only essential data is sent to the cloud or data center, minimizing network traffic. This efficient use of bandwidth is crucial in environments with limited network resources or where data transmission costs are a concern, optimizing network usage and reducing costs.
Improved Reliability: By spreading computing resources across several locations, edge computing diminishes the likelihood of a complete system failure. This architecture boosts system reliability and ensures operations continue smoothly, even during network disruptions or cloud connectivity issues, by providing fault tolerance and enhancing overall system resilience.
Data Privacy and Security: Edge computing processes and stores sensitive information locally, thereby limiting its transmission over vulnerable networks. This approach strengthens data security and privacy, protecting against cyber threats and ensuring adherence to data protection regulations by keeping data within regional boundaries.
Scalability and Flexibility: Offering the ability to dynamically adjust computing resources as per demand, edge computing supports scalability and flexibility. It allows for the rapid deployment and scaling of edge nodes to meet application changes, facilitating resource management and business adaptation without significant infrastructure overhaul.
The combination of these benefits positions edge computing as a compelling choice for various applications, from IoT and real-time analytics to content delivery and applications demanding utmost reliability and minimal latency, underscoring its pivotal role in modern digital strategies.
Edge Computing is Ideal for Processing Data in Real-Time
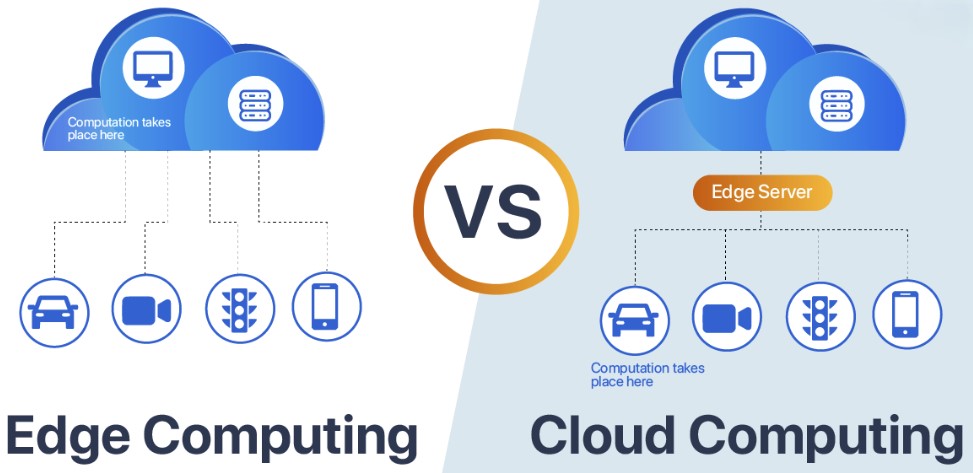
The main difference is responsiveness: edge computing is ideal for processing data in real-time, while cloud computing is better suited for processing voluminous information that is not time-sensitive. These computing platforms have individual and joint applications in a wide variety of futuristic scenarios.
Beyond Enhancing Processes to Redefining Industry Potential
Edge computing is changing more than just the way we handle data; it's opening up new possibilities in many fields. It's especially useful when quick data processing is needed because it doesn't rely on sending data far away to a cloud or data center. Let's explore the unique benefits edge computing offers, highlighting its critical impact on the future of data-driven industries:

Smart Cities: To manage urban infrastructure efficiently and enhance public safety. Edge computing processes data from IoT devices like traffic lights and air quality sensors in real-time. Improves traffic flow, reduces pollution, and enhances emergency response times.
Manufacturing: For predictive maintenance and optimizing production lines. Edge devices analyze data directly from manufacturing equipment to predict failures and adjust processes instantly. Minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and increases production efficiency.
Healthcare: To support remote patient monitoring and emergency medical services. Wearable devices and medical equipment use edge computing to process health data on-the-spot. nables real-time health monitoring, quickens emergency responses, and improves patient outcomes.
Retail: For enhancing customer experiences and operational efficiency. Edge computing analyses shopper behavior and inventory levels directly in-store. Personalizes shopping experiences, optimizes inventory management, and reduces checkout times.
Energy: For real-time monitoring and management of energy distribution. Edge computing enables smart grids to instantly process data from meters and sensors across the network. Optimizes energy distribution, reduces outages, and supports renewable energy integration.
Automotive: To support autonomous driving and in-vehicle entertainment systems. Edge computing processes data from vehicle sensors and cameras in real-time for decision-making. Enhances vehicle safety, improves navigation, and provides seamless entertainment experiences.
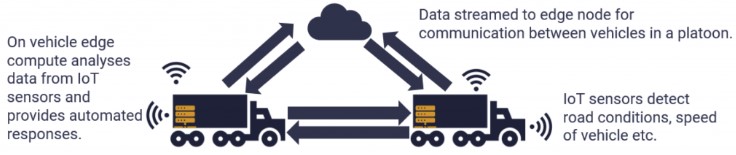
Edge computing thus unlocks vast potential across industries, enabling organizations to more effectively and efficiently utilize data at the network's edge.
Edge Computing Spending 2024
The worldwide edge computing market will reach $250. Billion in 2024 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% over the forecast period.
45.5% U.S. Market CAGR 2024-2023
Key trends include Edge AI, which moves computing closer to edge devices for quicker data processing and reduced latency. The introduction of 5G technology promises unprecedented speed and minimal latency, enhancing communication. IoT technology drives better connectivity and data sharing, facilitating efficient data collection and decisions. Real-time edge analytics allow for instant operational insights, while blockchain technology secures data in edge environments. Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) alleviates network congestion by introducing cloud functionalities nearer to data sources. Edge data centers and IT/OT Convergence improve local data handling and operational efficiency, respectively. Similarly, fog computing decentralizes processing and storage, optimizing data proximity.

Schrijf in voor onze Nieuwsbrief
Hebt u vragen of hulp nodig? Wij helpen u graag.
